
In terms of instrument analysis, ED-XRF (X-ray fluorescence spectrometer) and CIC (ion analyzer) are the most commonly used analytical instruments for analyzing halogen concentration. The X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer (XRF) uses the X-ray beam to irradiate the test piece to excite the elements in the test piece. When the self excited state of the atom returns to the ground state, it detects the released fluorescence. After analyzing its energy and intensity through the spectrometer, it can provide the type and content of the constituent elements in the test piece. Ion chromatography is an analytical method that uses the principle of ion exchange to separate the ions to be determined with different affinities between the mobile phase and the stationary phase, uses conductivity detector to determine, determines qualitatively according to the retention time of each component, and uses chromatographic peak area to quantify. The detection limit can reach the analytical level of ppb. At present, according to BS EN14582:2007 standard, oxygen bomb combustion uses ion chromatograph to analyze halogen.
Following the lead-free process, a new wave of green electronics - Halogen-free will once again sweep the global electronics industry. In the Norwegian PoHS Act, which is about to be implemented, 18 kinds of harmful substances that must be excluded have been clearly regulated. The first group is brominated flame retardants, including hexacyclic bromidedecane (HBCDD) and printed circuit boards. The most commonly used tetrabromopropanediol (TBBPA) and so on. In addition to the international laws that will be enacted successively, major international manufacturers including ASUS, Dell, HP, Apple, Intel, AMD and other companies have also declared that they will introduce halogen-free materials from 2008.
Halogen materials refer to fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), (At) in the periodic table, mainly for the function of flame retardancy, and are widely used in electronic equipment and other Accessories include machine boxes, printed circuit boards, cable wires, plastic parts and packaging materials. Electronic components and materials, bonding technology of electronic products, product housing (Housing), PP, ABS, PMMA, PC..., plastics, pigments, etc.
The hazards of halogens are also well known. Organohalogen compounds can cause cancer in the human body, and their low biodegradation rate will lead to accumulation in the ecosystem. Some volatile organic halogen compounds also have a great destructive effect on the ozone layer, which in turn affects the environment. Therefore, halogen compounds are listed as chemicals harmful to humans and the environment, and their use is prohibited or limited.
Following the lead-free process, a new wave of green electronics halogen-free will once again sweep the global electronics industry. In the upcoming Norwegian PoHS Act, 18 hazardous substances that must be excluded have been specified. The first group is brominated flame retardants, including hexacyclobromododecane (HBCDD) and tetrabromopropanol (TBBPA), which are most commonly used in printed circuit boards. In addition to the international laws that will be enacted in succession, international manufacturers including ASUS, Dell, HP, Apple, Intel, AMD and other companies also announced that they will import halogen-free materials from 2008.
Halogen materials refer to fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I) and (At) in the periodic table. They are mainly used for flame retardancy and are widely used in electronic equipment and its accessories, including machine boxes, printed circuit boards, cable wires, plastic parts and packaging materials. Electronic components and materials, bonding technology of electronic products, housing, PP, ABS, PMMA, PC..., plastics, pigments, etc.
The hazards of halogens are also well known. Organic halogens can cause cancer in the human body, and their low biodegradation rate will lead to the accumulation in the ecosystem. Some volatile organic halogens also have a great destructive effect on the ozone layer, thus causing serious impact on the environment and human health. Therefore, halogens are listed as chemicals harmful to humans and the environment, and their use is prohibited or limited.
International specifications such as halogen materials
From Freon to POPs, from PVC to brominated flame retardant (BFR), it is an indisputable fact that organic halides are harmful to human body and natural ecological environment. The Montreal Protocol signed in 1987 and the Stockholm Convention signed in 2001 show that countries around the world have restricted the production and use of such substances. In recent years, the well-known EU Directive on the Prohibition of Electrical and Electronic Hazards (ROHS Directive) stipulates that bromine flame retardants will be banned from July 1, 2006. At the same time, there are a series of international laws and regulations prohibiting the use of some toxic and harmful halogenated organic solvents on electronic appliances, toys and leather products, including the prohibition of use in the production and processing process, the prohibition of residues in the final product, and the limitation of volatile halogenated organic substances in the final product.
International organizations or large manufacturers such as IEC, IPC, JPCA and Samsung have defined the specifications of their halogen-free materials. The IEC 61249-2-21 specification requires that the content of bromine and chloride must be less than 900 ppm, and the total halogen content must be less than 1500 ppm. The definition of halogen-free materials in IPC is the same as that in IEC; The JPCA specification defines that the limit of bromide and chloride content is 900 ppm, and does not require the total halogen content. Samsung stipulates that the content limit of bromide and chloride is 900 ppm respectively.
Definitions of International Electrotechnical Association IEC 61249-2-21: 2003∶
Substance | Permissible Limit (by weight) |
Bromine (Br) | 900 ppm (0.09%) |
Chlorine (Cl) | 900ppm (0.09%) |
Total concentration of: chlorine (Cl) + bromine (Br) | 1500ppm (0.15%) |
Table 1. Specifications of halogen-free materials of International Electrotechnical Association IEC 61249-2-21: 2003
Ion chromatography analysis method:
1. Sample treatment: oxygen bomb burning or oxygen bottle burning
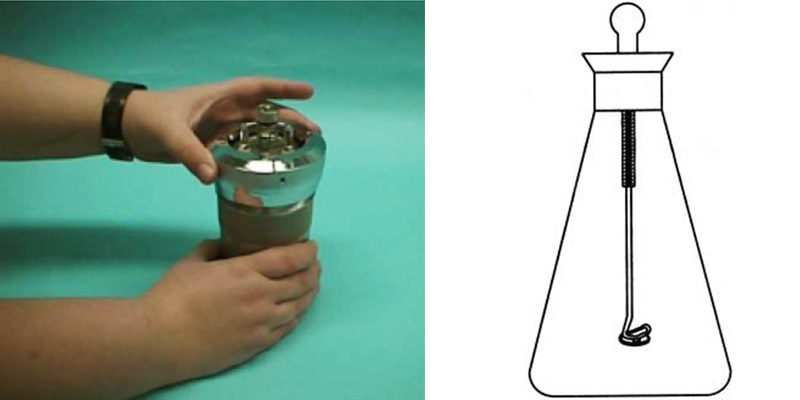
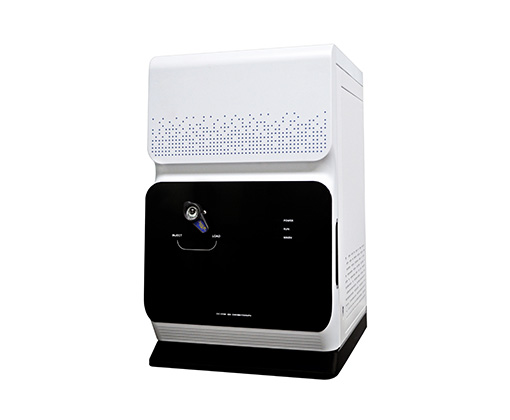
2. Ion chromatograph:
CIC100 standard ion chromatograph
According to WEEE directive and IEC/EN1249-2-21 standard, only when the bromine ion content in PCB substrate does not exceed 900 PPM, the chloride ion content does not exceed 900 PPM, and the bromine+chloride ion content does not exceed 1500 PPM, can PCB be called halogen-free.
Test standard: EN14582 or IEC61189-2006. Ion chromatography is recommended internationally for detection, and oxygen bomb combustion conversion is recommended for pretreatment. Take CIC100 ion chromatography as an example:
2. Practical Application Report
Overview: Halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine) are added to polymer products such as plastics to improve the ignition point. Its advantages are: the ignition point is higher than that of ordinary polymer materials, and the ignition point is about 300 ℃. During combustion, halogenated gases (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine) will be emitted, and oxygen will be quickly absorbed to extinguish the fire. However, its disadvantage is that when the concentration of chlorine released is high, the visibility will be reduced, which will lead to the inability to identify the escape path. At the same time, chlorine has a strong toxicity, which affects the respiratory system of people. In addition, the halogen gas released from the combustion of halogenated polymers will generate corrosive harmful gas (hydrogen halide) when combined with water vapor, causing corrosion to some equipment and buildings.
Brominated flame retardants, such as PBB, PBDE, TBBPA, are widely used in electronic and electrical industries, including circuit boards, computers, fuel cells, televisions and printers.
These halogenated flame retardant materials produce dioxins when burning, and can exist in the environment for many years, or even accumulate in organisms for life, and cannot be discharged.
At present, different products have different limit standards for halogen-free requirements:
For example, the halogen index of halogen-free wires and cables is: the value of all halogens ≤ 50PPM
(according to the regulation PREN 14582); Content of hydrogen halide gas generated after combustion < 100PPM
(according to EN 5067-2-1); PH value of hydrogen halide gas generated after combustion after being dissolved in water ≥ 4.3
(according to EN-5 0267-2-2); The light transmittance of the product after burning in a closed container is ≥ 60%
(according to EN-50268-2).
Detection and analysis spectrogram of halogen in plastics:
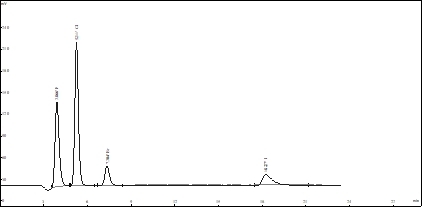
The above figure shows the detection spectrum of halogen content in a packaging plastic, corresponding to F -, CL -, Br -, I -, four halogen ions. It is a convenient and fast international standard analysis method, which can complete the analysis and detection within 20 minutes after one sample injection.
1. High pressure pump with wide range, high performance and low pulse double flow reviving plug is used, and the pump speed reaches 9.999ml/min
2. It can support a variety of anion/cation chromatographic columns at home and abroad, with high reliability and stability, accurate flow and low maintenance Equal advantages
3. The advanced online degassing technology can conduct real-time degassing control for the mobile phase, avoiding the tedious operation and intermittence of the traditional degassing pump.
4. The advanced continuous automatic regeneration membrane suppressor has high inhibition capacity, no need to use a peristaltic pump, fast balance, anti pollution, good repeatability, no need to use any consumables, and zero maintenance.
The design and manufacture of ion chromatograph shall comply with the national standard. The main design and manufacturing standards and specifications are as follows: (List the standard number and standard name)
Serial No | Standard name | Standard No |
1 | WEEE Directive | EN61010-1: 1993 |
2 | IEC/EN 1249 2-21 | EN50081-1: 1992: |
3 | Standard method for hygienic examination of sulfate in air of residential areas - ion chromatography | GB/T11733-89 |
4 | Determination of fluoride, chlorine, nitrite, nitrate and sulfate in atmospheric precipitation by ion chromatography | GB13580.5-92 |
5 | Industrial circulating cooling water Determination of sodium, ammonium, potassium, magnesium and calcium ions Ion chromatography | GB/T15454-95 |
6 | Industrial circulating cooling water and boiler water Determination of fluoride, chlorine, phosphate, nitrite, nitrate and sulfate ion chromatography | GB/T14642-93 |
7 | Determination of trace chloride, nitrate, phosphate and sulfate ions in electronic grade water by ion chromatography | GB/T11446.7-1997 |
8 | Test methods for drinking natural mineral water (including 25.3 ion chromatography of lithium, 36.3 ion chromatography of fluoride, 37.2 ion chromatography of chloride, 38.1 ion chromatography of bromide, 39.3 ion chromatography of iodide, and ion chromatography of nitrate) | GB/T8538-1995 |
9 | Separation and Determination of Phosphates in Detergents (Ion Exchange Column Chromatography) | GB/T13173.4-91 |
10 | Determination of non-ionic surfactant content in detergents (ion exchange method) | GB/T13173.3-91 |
11 | Separation and determination of different forms of phosphate by industrial sodium tripolyphosphate ion exchange column chromatography, which was drafted according to ISO 3358:1979 "Separation and determination of different forms of phosphateby industrial sodium tripolyphosphate and sodium pyrophosphate ion exchange column chromatography" | GB/T9984.3-2004 |
12 | Inspection methods for groundwater quality Determination of chloride, fluoride, bromine, nitrate and sulfate by ion chromatography | DZ/T0064.51-93 |
13 | Test methods for groundwater quality -- Determination of potassium, sodium, lithium and ammonium by ion chromatography | DZ/T0064.28-93 |
14 | Determination of sodium, magnesium and calcium in urban water supply by ion chromatography | CJ/T143-2001 |
15 | National Metrological Verification Regulation of the People's Republic of China - Ion Chromatograph | JJG 823-93 |
16 | Determination of Inorganic Trace Anions in Steam of Thermal Power Plant | DL/T954-2005 |
Equipment name and model | Halogen special instrument | |
purpose | Suitable for the analysis of halogen ions in various samples | |
quantity | 1 set | |
Operating ambient temperature | 15 to 30 ℃ | |
pump | ||
project | explain | data description |
Double piston tandem high-pressure pump | Yes or No | Yes |
Maximum pressure | Mpa | 42 Mpa |
Flow rate range | ml/min | 0.001-9.999 |
Flow rate increment | ml | 0.01 |
Flow accuracy | % | 0.2% |
Pump head volume | mL | 10 |
Solenoid six way valve | Yes or No | yes |
Eluent system | sodium carbonate | |
Nitrogen required | Yes or No | no |
Conductivity detector | ||
Conductivity detector | Pentapolar conductance | |
Volume of conductivity cell | uL | <1.0 uL |
Detector range | us/cm | 0—1000 |
Maximum electron drift | FS | 2.0% |
Electronic noise | FS | 1.0% |
resolving power | ns/cm | 0.05ns |
Pretreatment | ||
Oxygen bomb combustion device | Sufficient treatment of samples | |
Needle filter | 0.22um | Filter the suspended impurities in the sample |
C18 column | Adsorption of organic matters | |
On-line degassing | Real time degassing of mobile phase | |
Analysis system | ||
Type of suppressor | Membrane suppressor | |
Structural design of suppressor | Continuous automatic regeneration | |
Continuous suppression | Continuous automatic suppression | |
Electrolytic regeneration | Yes or No | yes |
Suppress repeatability | Good repeatability | |
Inhibition ability | Strong inhibition, 50 times of column inhibition | |
Ion analysis column compatibility | Compatible with various columns | |
PH resistance range of analytical column | 0-14 | |
Ion analysis column selection | Wide selectivity | |
Anion analysis type | F-,Cl-,Br-,I- | |
Chinese software | Chinese and English software | |
Free warranty period of the whole machine | 1 year | |
Main configuration | Specification and model | quantity |
host | CIC-D100 | 1 set |
High pressure double plunger advection pump | UA-100A | 1 set |
Six way sampling valve | --- | 1 set |
Conductivity detector | SHD-3 | 1 set |
Anion chromatographic column | SH-AC-3 | 1 set |
Anion protection column | SH-G-1 | 1 set |
Oxygen bomb combustion device (optional) | SH-YS-1 | 1 set |
Anion suppression system | SHY-A | 1 set |
Flow path system | Peek | 1 set |
Sand core filter | SHF | 1 set |
Chromatographic workstation | SH010 | 1 set |
spare parts | SH000 | 1 batch |
Computer and printer (optional) | / | 1 set |
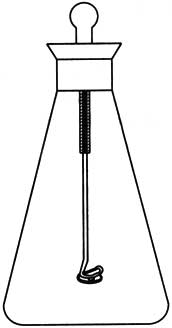
Oxygen cylinder combustion method
1. Oxygen cylinder combustion method: A 500mL iodine measuring bottle is connected with a section of platinum wire with spiral lower end at the center of the grinding plug. The diameter of platinum wire is about 1mm (see the figure below)
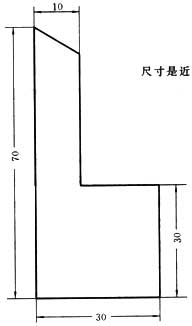
2. Shape of sample wrapping paper for oxygen flask combustion method (ashless filter paper)
1. Sample pretreatment steps:
1. Cut 0.5-2.0g sample according to the expected amount of halogen, and cut it into small pieces less than 1mm on each side.
2. Weigh 40~50mg sample, accurate to 0.1mg. If the halogen content is known to be small, several samples can be burned continuously on the same absorption solution in the same absorption bottle. The samples are wrapped with filter paper, sandwiched in the spiral platinum wire, and the leaching solution (30-50ml) is added in the oxygen combustion bottle.
3. Put it in the safety cover. Connect the oxygen cylinder and apply oxygen at a flow rate of at least 2L/min for 1min. When the combustion cylinder is filled with oxygen, ignite the end of the filter paper of the package sample, quickly disconnect and open the oxygen system, cover the bottle plug, and press it tightly by hand. It can be removed from the safety cover only after the flame is extinguished. There should be no black ash residue in the bottle.
4. Park for about 10min, open the bottle stopper, and rinse the bottle stopper and platinum wire with appropriate amount of eluent.
2. Operation steps of ion chromatograph
1. Transfer the absorption solution to a 100ml volumetric flask and fix the volume. 2. The sample is analyzed by ion chromatography. We will provide on-site installation training for professional technicians, which is a very simple process and lasts for 3-5 days.